Day 11: Extensions
Add custom methods to ANY type (String, int, BuildContext) without touching the original code. Write cleaner, smarter Flutter apps!
မင်္ဂလာပါ.. 👋
100 days of Flutter ရဲ့ Day 11 က ကြိုဆိုပါတယ်။ ဒီနေ့မှာတော့ dart langauge နဲ့ ပတ်သက်တာတွေကို ဆက်လက်ပြီး လေ့လာသွားပါမယ်။ ဒီနေ့ဆွေးနွေးသွားမယ့် ခေါင်းစဥ်ကတော့ Extensions ပဲ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။
ဒီနေ့မှာတော့ dart language ရဲ့ feature တခုလို့ ပြောလို့ရတဲ့ extension အကြောင်းနဲ့ မိတ်ဆက်ပေးချင်ပါတယ်။ ဒါကိုနားလည်ခြင်းအားဖြင့် app တွေရေးတဲ့အခါ ပိုပြီး professional ကျကျ ရေးသွားနိုင်မှာပဲ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။
အခုလောလောဆယ် e-commerce app တခု တည်ဆောက်နေတယ်လို့ တွေးကြည့်ကြပါစို့။ app မှာ ဈေးတွေကို မြန်မာငွေအဖြစ်နဲ့ ပြပေးတာ၊ email valiate လုပ်တာ၊ password strength စစ်တာ၊ date/time တွေကို readable ဖြစ်အောင် ပြပေးတာ စသဖြင့် ပါဝင်မှာပဲ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ ပုံမှန် ရေးနည်းအတိုင်း ရေးမယ်ဆို အခုလိုမျိုး utility classes တွေနဲ့ရေးတာ မြင်ဖူးကြပါလိမ့်မယ်။
class StringUtils {
static bool validateEmail(String email) {
return RegExp(r"^[a-zA-Z0-9.]+@[a-zA-Z0-9]+\.[a-zA-Z]+").hasMatch(email);
}
static bool isStrongPassword(String password) {
return password.length >= 8 &&
password.contains(RegExp(r'[A-Z]')) &&
password.contains(RegExp(r'[0-9]'));
}
static String capitalize(String text) {
return text[0].toUpperCase() + text.substring(1);
}
}
class CurrencyUtils {
static String formatKyat(int amount) {
return '$amount Kyats';
}
static String formatKyatWithCommas(int amount) {
return '${_addCommas(amount)} Kyats';
}
static String _addCommas(int number) {
return number.toString().replaceAllMapped(
RegExp(r'(\d{1,3})(?=(\d{3})+(?!\d))'),
(Match m) => '${m[1]},',
);
}
}
class DateUtils {
static String toReadable(DateTime date) {
return '${date.day}/${date.month}/${date.year}';
}
static bool isToday(DateTime date) {
final now = DateTime.now();
return date.day == now.day &&
date.month == now.month &&
date.year == now.year;
}
}
void processCheckout(String email, int price, DateTime orderDate) {
if (StringUtils.validateEmail(email)) {
print('Processing order for ${CurrencyUtils.formatKyatWithCommas(price)}');
print('Order date: ${DateUtils.toReadable(orderDate)}');
}
}
void main() {
final email = 'aung@aung.com';
final price = 1000;
final orderDate = DateTime.now();
processCheckout(email, price, orderDate);
}
// Output:
// Processing order for 1000 Kyats
// Order date: 11/1/2026အပေါ်မှာပေးထားတာ ကြည့်မယ်ဆို StringUtils, CurrencyUtils နဲ့ DateUtils ဆိုပြီး utility class ၃ခုကို တွေ့ရမှာပါ။ အခုလို ရေးထားခြင်းအားဖြင့် utility class တွေ ရှိနေတာ အမှတ်ရနေဖို့လိုပြီး utility class တွေကို သုံးမယ့်နေရာတိုင်းမှာ import လုပ်ပေးနေဖို့ လိုပါလိမ့်မယ်။
ဒီမှာ static ဆိုတဲ့ အသုံးအနှုန်းကိုလဲ သတိထားမိပါလိမ့်မယ်။ ဒါကတော့ class တွေထဲမှာ ကြေငြာထားတဲ့ method တွေ၊ parameter တွေကို object တွေ တည်ဆောက်စရာမလိုဘဲ သုံးနိုင်အောင် လုပ်ပေးထားတာပဲ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။RegExp နဲ့ပတ်သက်တာတွေကိုတော့ အသေးစိတ် article သပ်သပ်နဲ့ ရှင်းပြပေးပါ့မယ်။ အခု လောလောဆယ် သိချင်တယ်ဆိုရင်တော့ https://regex101.com/ မှာ လေ့လာလို့ရပါတယ်။
ဒီတော့ အဲ့လိုမျိုး utility class တွေအစား တခြားရေးတဲ့နည်းကို လေ့လာကြည့်ရအောင်ပါ။ အဲ့ဒါကိုတော့ dart extension လို့ခေါ်ပါတယ်။
Open-Closed Principle
ဒါကတော့ အခြေခံ software engineering principle တွေထဲက တခုပဲ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။
Software entities should be open for extension but closed for modification.
Extension ဆိုတာကတော့ ဒီ principle ပေါ် အခြေခံပြီး တည်ဆောက်ထားတာ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ သူ့ကို သုံးပြီးတော့ နဂိုမူလ ရှိပြီးသားကိုသွားပြီး ပြင်ဆင်စရာမလိုဘဲ implementation အသစ်တွေကို ထည့်လို့ရသွားမှာ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ utility class တွေလိုမျိုးလဲ သပ်သပ်ကြီး ရှိနေစရာမလိုဘဲ လက်ရှိရှိပြီးသား type နဲ့ အလိုအလျှောက် ဆက်စပ်ပေးသွားနိုင်မှာပဲ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ editor ကလဲ auto complete လုပ်ဖို့ ပြပေးနေမှာ ဖြစ်တဲ့အတွက် development အတွက်လဲ အများကြီး အထောက်အကူ ပြုပါတယ်။
extension <Name> on <Type> {}extension ကိုရေးမယ်ဆို အပေါ်မှာပြထားတဲ့ format အတိုင်းရေးပါတယ်။ တကယ်လို့ extension ကို သူ့ကို ရေးထားတဲ့ file ထဲမှာပဲ သုံးမယ်ဆို နာမည်မထည့်ပေးလဲ ရပါတယ်။ on keyword ရဲ့ နောက်မှာ ပါတဲ့ Type ကတော့ String, int, double စသဖြင့် data type တွေဖြစ်စေ၊ ကိုယ်ကြေငြာထားတဲ့ class တွေဖြစ်စေ အသုံးပြုလို့ရပါတယ်။ Data type တွေ အတွက်တော့ အသုံးများပါတယ်။
extension on <Type> {}အရင်ဆုံး String အတွက် အပေါ်မှာ ပြခဲ့တဲ့ utility class က method တွေကို extension အနေနဲ့ ဘယ်လို ရေးလို့ရမလဲ ကြည့်ရအောင်ပါ။ StringUtils ထဲမှာ ရှိတဲ့ method တွေကို ခေါ်တဲ့အခါ String value ထည့်ပေးတာကို ကြည့်ခြင်းအားဖြင့် String data type ပေါ်မှာ extension အနေနဲ့ ရေးပေးဖို့လိုတာကို တွေ့ရမှာပါ။
extension StringExtension on String {
bool get isValidEmail {
return RegExp(r"^[a-zA-Z0-9.]+@[a-zA-Z0-9]+\.[a-zA-Z]+").hasMatch(this);
}
bool get isStrongPassword {
if (length < 8) return false;
if (!contains(RegExp(r'[A-Z]'))) return false;
if (!contains(RegExp(r'[a-z]'))) return false;
if (!contains(RegExp(r'[0-9]'))) return false;
return true;
}
String get capitalize {
if (isEmpty) return this;
return '${this[0].toUpperCase()}${substring(1).toLowerCase()}';
}
String truncate(int maxLength, {String ellipsis = '...'}) {
if (length <= maxLength) return this;
return '${substring(0, maxLength - ellipsis.length)}$ellipsis';
}
}
Utility class ထဲမှာ ရေးထားတဲ့ method တွေကို extension ထဲမှာတော့ getter တွေ အနေနဲ့ ပြောင်းရေးလိုက်တာကို တွေ့ရမှာပါ။ ဒါကတော့ value တခုထဲကို အခြေခံလို့ပဲ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ တကယ်လို့ တခြား value တွေပါ ထည့်ပေးဖို့ လိုတယ်၊ runtime မှပဲ သိရတာမျိုး ဖြစ်မယ်ဆိုရင် method အနေနဲ့ကြေငြာလို့ရပါတယ်။ extension ထဲမှာတော့ ဝင်လာတဲ့ value ကို access လုပ်ချင်တဲ့အခါ this ဆိုပြီးတော့ သုံးပါတယ်။ သူ့ရဲ့ method တွေ, getter တွေကို သုံးဖို့လိုတဲ့အခါ this ကို သုံးလို့ရသလို မသုံးဘဲလဲတန်းခေါ်လို့ ရပါတယ်။ အပေါ်မှာ length, contains, isEmpty စသဖြင့် သုံးထားတာတွေကို တွေ့ရမှာပါ။ this.length လို့ မရေးဘဲ length လို့ရေးလိုက်တာက extension ရဲ့ type ကို သွားပြီး reference လုပ်ပေးနေမှာပါ။ ဒီလို method တွေ၊ getter တွေကလဲ ဘယ် data type ပေါ် extension လုပ်တာလဲဆိုတာ ပေါ် မူတည်ပါတယ်။
import 'string_extension.dart';
void main() {
String email = 'aung@aung.com';
print(email.isValidEmail);
String password = 'password';
print(password.isStrongPassword);
String name = 'this is cool!';
print(name.capitalize);
String longString = 'This is a very long text that needs truncation';
print(longString.truncate(10));
print(longString.truncate(10, ellipsis: '>>>'));
}
// Output:
// true
// false
// This is cool!
// This is...
// This is>>>extension ကြေငြာပြီးလို့ သုံးချင်တယ်ဆိုလဲ ပုံမှန် getter တွေ၊ method တွေလိုမျိုး သုံးလို့ရပါတယ်။ extension ကို import မလုပ်ထားရင်တောင် dart ရဲ့ autocomplete မှာ getter တွေ၊ method တွေ ပြနေမှာဖြစ်ပြီး ကိုယ်က ရွေးလိုက်တဲ့အခါ အလိုအလျောက် import လုပ်ပေးသွားမှာပါ။ တကယ်လို့ auto complete မပြတာ auto import မလုပ်ပေးတာတွေ ရှိခဲ့ရင်လဲ ကိုယ်တိုင် import လုပ်လိုက်လို့လဲ ရပါတယ်။
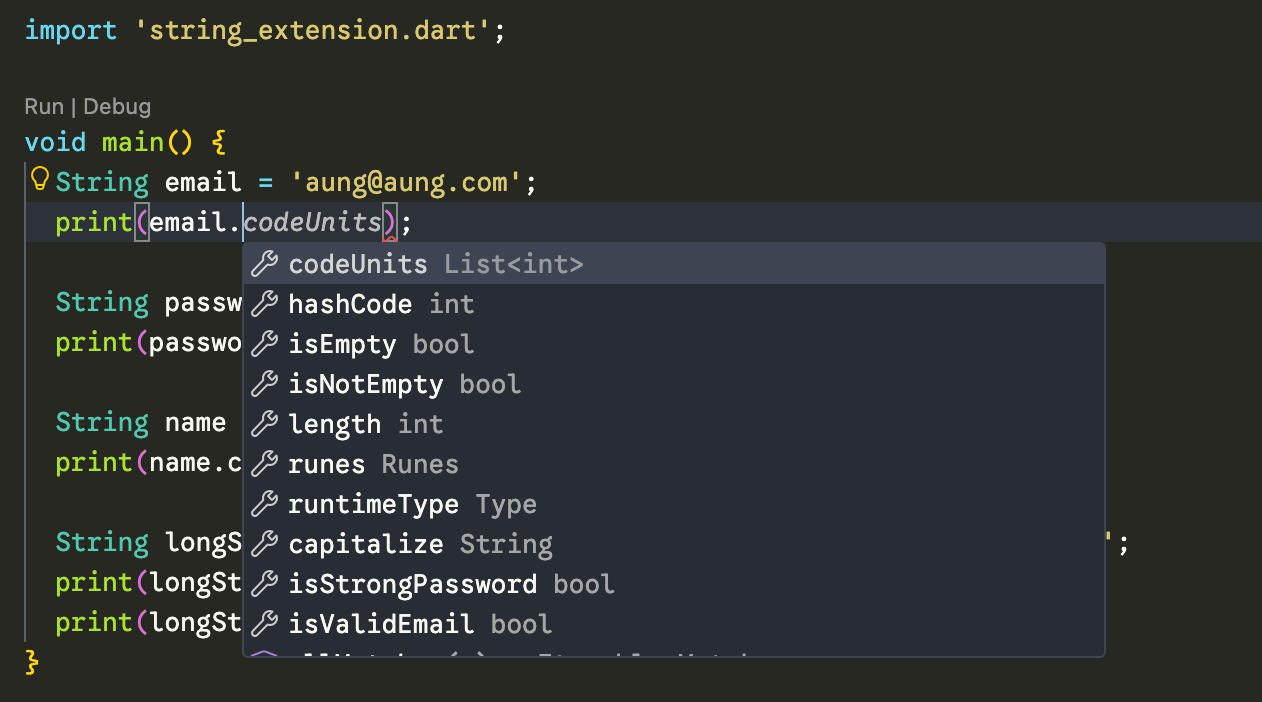
ဒါဆိုရင်တော့ extension ဆိုတာဘာလဲ အကြမ်းဖျင်းသိလောက်ပြီ ထင်ပါတယ်။
ဆက်ပြီးတော့ အပေါ်မှာ ရှိတဲ့ CurrencyUtils နဲ့ DateUtils တို့အတွက် ဆက်ကြည့်လိုက်ရအောင်ပါ။
extension IntExtension on int {
String get formatKyat {
return '$this Kyats';
}
String get formatKyatWithCommas {
return '${_addCommas(this)} Kyats';
}
String _addCommas(int number) {
return number.toString().replaceAllMapped(
RegExp(r'(\d{1,3})(?=(\d{3})+(?!\d))'),
(Match m) => '${m[1]},',
);
}
}
void main() {
final amount = 1000000;
print(amount.formatKyat);
print(amount.formatKyatWithCommas);
}
// Output:
// 1000000 Kyats
// 1,000,000 Kyatsဒါကတော့ int data type နဲ့ ပတ်သက်ပြီး extension တွေ ထပ်ထည့်ထားတာ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ ဒီမှာကြည့်မယ်ဆို getter ကနေတဆင့် private method လိုမျိုးတွေလဲ ကြေငြာပြီး သုံးလို့ရတာကို တွေ့ရမှာပါ။
extension DatetimeExtension on DateTime {
String get toReadable {
return '$day/$month/$year';
}
bool get isToday {
final now = DateTime.now();
return day == now.day && month == now.month && year == now.year;
}
}
void main() {
final orderDate = DateTime(2026, 1, 11);
print(orderDate.toReadable);
print(orderDate.isToday);
}
// Output:
// 11/1/2026
// trueဒါကတော့ DateTime data type နဲ့ ပတ်သက်ပြီး extension တွေ ထပ်ထည့်ထားတာ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။
extension ListExtensions<T> on List<T> {
T? get firstOrNull => isEmpty ? null : first;
T? get lastOrNull => isEmpty ? null : last;
List<T> get unique => toSet().toList();
List<List<T>> chunk(int size) {
List<List<T>> chunks = [];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i += size) {
chunks.add(sublist(i, i + size > length ? length : i + size));
}
return chunks;
}
}
extension IntListExtensions on List<int> {
double get average {
if (isEmpty) return 0;
return reduce((a, b) => a + b) / length;
}
int get sum => isEmpty ? 0 : reduce((a, b) => a + b);
int? get maxValue => isEmpty ? null : reduce((a, b) => a > b ? a : b);
int? get minValue => isEmpty ? null : reduce((a, b) => a < b ? a : b);
}
extension StringListExtensions on List<String> {
String get toOxfordComma {
if (isEmpty) return '';
if (length == 1) return first;
if (length == 2) return '$first and $last';
return '${sublist(0, length - 1).join(', ')}, and $last';
}
}
void main() {
List<int> scores = [85, 92, 78, 92, 85, 95];
List<String> names = ['Aung', 'Kyaw', 'Zaw'];
print(scores.average); // 87.83
print(scores.unique); // [85, 92, 78, 95]
print(scores.maxValue); // 95
print(names.toOxfordComma); // "Aung, Kyaw, and Zaw"
List<int> items = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9];
print(items.chunk(3)); // [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
}
ဒီမှာတော့ ဘယ်လို List type မဆို အသုံးပြုနိုင်မယ့် extension တွေ လိုချင်တဲ့အခါ အသုံးပြုလို့ရမယ့် generic type list List<T> ဆိုပြီးတော့ တွေ့ရမှာပါ။ ပြီးတော့ List type တခုချင်းစီမှာ သုံးလို့ရမယ့် type specific list List<String>, List<int> တွေကိုလဲ တွေ့ရမှာပါ။
extension MyanmarValidators on String {
// Myanmar National Registration Card (NRC)
// Format: 12/MaKaNa(N)123456
bool get isValidNRC {
return RegExp(
r'^\d{1,2}/[A-Z][a-z]{2}[A-Z][a-z]{2}\([NC]\)\d{6}$'
).hasMatch(this);
}
// Myanmar Postal Code (5 digits)
bool get isValidPostalCode {
return RegExp(r'^\d{5}$').hasMatch(this);
}
// Myanmar Unicode text detection
bool get containsMyanmarText {
return RegExp(r'[\u1000-\u109F]').hasMatch(this);
}
}
ဒါကတော့ မြန်မာပြည်အတွက် app တွေ ရေးတဲ့အခါ သုံးနိုင်တဲ့ extension နမူနာလေးပဲ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။
ဒီတော့ extension method တွေဆိုတာ ကိုယ်သုံးချင်တဲ့ data type ပေါ်မူတည်ပြီး တည်ဆောက်လို့ရတာကို တွေ့ရမှာ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ User-defined data type တွေမှာလဲ extension တွေကို သုံးလို့ရပါတယ်။
class User {
final String firstName;
final String lastName;
final DateTime birthDate;
User(this.firstName, this.lastName, this.birthDate);
String get fullName => '$firstName $lastName';
int get age {
final today = DateTime.now();
return today.year - birthDate.year;
}
bool get isAdult => age >= 18;
}
extension UserExtensions on User {
String get initials => '${firstName[0]}${lastName[0]}'.toUpperCase();
String greet() {
final hour = DateTime.now().hour;
if (hour < 12) return 'Good morning, $firstName!';
return 'Good evening, $firstName!';
}
}
void main() {
final user = User('Aung', 'Aung', DateTime(2000, 1, 1));
print('fullname: ${user.fullName}');
print('age: ${user.age}');
print('isAdult: ${user.isAdult}');
print('initials: ${user.initials}');
print(user.greet());
}
// Output:
// fullname: Aung Aung
// age: 26
// isAdult: true
// initials: AA
// Good evening, Aung!ဒီနေ့ Day 11 အတွက်ကတော့ ဒီလောက်ပဲ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ အဆုံးထိ ဖတ်ပေးတဲ့အတွက် အများကြီး ကျေးဇူးတင်ပါတယ်။ နားမလည်တာတွေ အဆင်မပြေတာတွေ ရှိခဲ့ရင်လဲ အောက်မှာပေးထားတဲ့ discord server ထဲမှာ လာရောက်ဆွေးနွေးနိုင်ပါတယ်။ နောက်နေ့တွေမှာလဲ ဆက်လက်ပြီး sharing လုပ်သွားပေးသွားမှာ ဖြစ်တဲ့အတွက် subscribe လုပ်ထားဖို့ ဖိတ်ခေါ်ပါတယ်။
- Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/@arkarmintun
- Newsletter: https://arkar.dev/
- Discord: https://discord.gg/3xUJ6k6dkH
