Day 5: Null Safety & The "Sound" System
Eliminate billion-dollar null pointer crashes forever by mastering Dart's sound null safety operators that make your apps incredibly stable.
မင်္ဂလာပါ.. 👋
100 days of Flutter ရဲ့ Day 5 က ကြိုဆိုပါတယ်။ ဒီနေ့မှာတော့ dart langauge နဲ့ ပတ်သက်တာတွေကို ဆက်လက်ပြီး လေ့လာသွားပါမယ်။ ဒီနေ့ဆွေးနွေးသွားမယ့် ခေါင်းစဥ်ကတော့ Null Safety အကြောင်းပဲ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။
Programming နဲ့ပတ်သက်ပြီး လုပ်ဖူးတဲ့သူတွေဆို Null Pointer Exception ကို ကြုံဖူးကြမယ်ထင်ပါတယ်။ value မရှိတဲ့ variable တွေကို access လုပ်မိတဲ့အခါ null pointer exception ဆိုပြီး ပေါ်လာတတ်ပါတယ်။ Exception ဖြစ်တဲ့အတွက် program တခုလုံး ရပ်သွားနိုင်တာမျိုး ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။
String username;
print(username.length);ဒီ code ကိုကြည့်မယ်ဆို variable ကို ကြေငြာတာ (definition) ပဲ လုပ်ပြီး ဘာ value မှ ထည့်မထား (assignment) တဲ့အတွက် run လိုက်တဲ့အခါ error ကြုံမှာပဲ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။
Dart programming language မှာလဲ အရင်တုန်းက null အတွက် support ကောင်းကောင်း မရှိတဲ့အတွက် app တွေ သုံးနေတုန်းမှာ null error တွေကြုံပြီး crush တာတွေ အထိ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ Programming language တခုအနေနဲ့ development လုပ်တဲ့အချိန်၊ compile လုပ်တဲ့အချိန်တွေမှာ အခုလို null exception ဖြစ်နိုင်ချေတွေကို ကြိုတင်ပြီး စစ်ဆေးတာမျိုး ရှိတယ်ဆို user တွေလက်ထဲရောက်မှ crush တာတွေကို အများကြီး လျှော့ချနိုင်မှာပဲ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။
Dart Version 2.12 ကစပြီးတော့ null safety အတွက် စပြီးတော့ support တွေ ထည့်ပေးလာပါတယ်။ Developer တွေကိုလဲ null safety ကို migrate လုပ်ဖို့ တိုက်တွန်းလာတာ အခု version 3 ရောက်တဲ့အခါမှာတော့ default အနေနဲ့ကို enforce လုပ်နေပါပြီ။
အပေါ်မှာ ပေးထားတဲ့ code ကိုပဲ null safety ဖြစ်တဲ့ version မှာ ရေးလိုက်တဲ့အခါ အခုလိုမျိုး တွေ့ရမှာပဲ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။
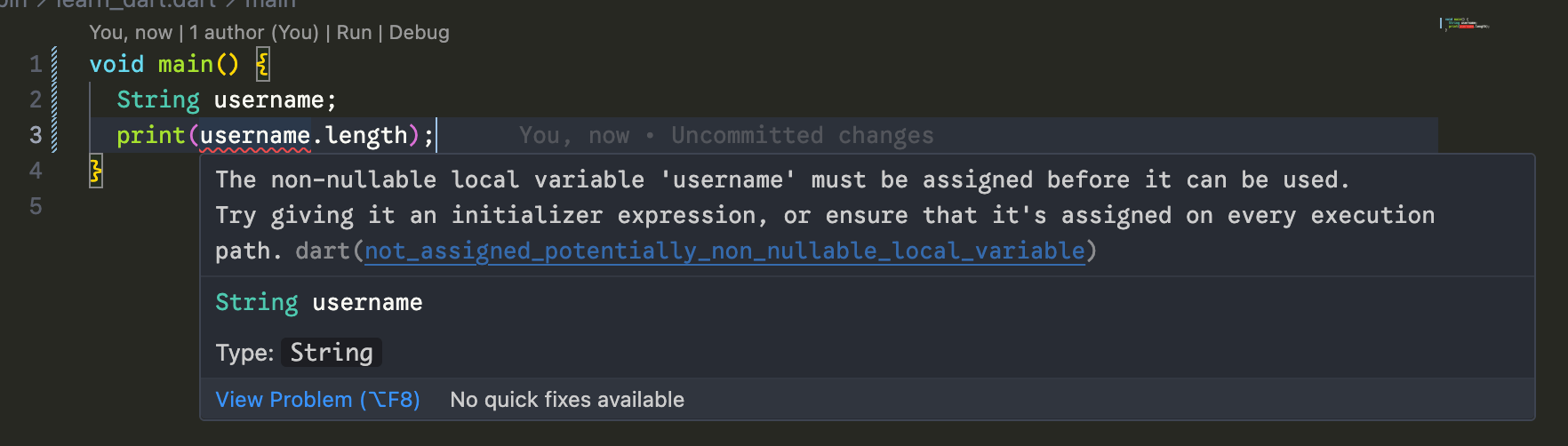
Nullable ဖြစ်နိုင်တယ်လို့ သတ်မှတ်မထားတဲ့ variable ကို ဘာ value မှ မသတ်မှတ်ခင် access လုပ်နေလို့ပဲ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။
Null ဖြစ်နိုင်တဲ့ variable တွေသတ်မှတ်ချင်တယ်ဆို nullable symbol ဖြစ်တဲ့ ? ကို ထည့်ပေးထားတော့မှ compile လုပ်လို့ရတော့မှာပါ (ဥပမာ - String?, int?, double?)။ Nullable မဟုတ်တဲ့ value တွေဆို null value ကို program ရဲ့ တနေရာရာမှာ မတော်တဆ assign လုပ်လို့တောင် ရမှာ မဟုတ်ပါဘူး။
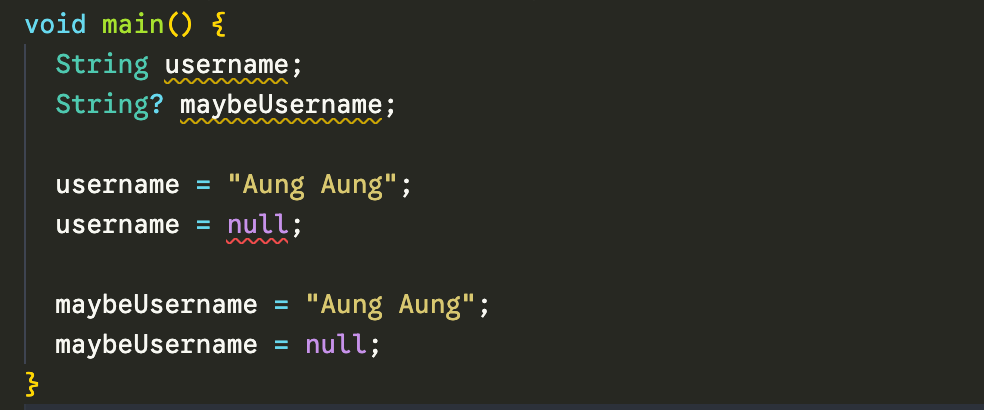
ဒီတော့ null exception ဘယ်တော့မှ မကြုံတော့ဘူးလားဆိုတော့ မဟုတ်ပါဘူး။ ဖြစ်နိုင်တဲ့ အခြေအနေမျိုးတွေ ရှိပါသေးတယ်။
အပေါ်မှာ ပြထားသလိုမျိုး non-nullable (String, int, double,...), nullable (String?, int?, double?,...) တို့အပြင် variable သတ်မှတ်တဲ့အချိန်မှာ သုံးလေ့ရှိတာ နောက်တခု ရှိပါသေးတယ်။ ဒါကတော့ late keyword ပဲ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။
late String username;
void main() {
print(username.length);
}အပေါ်မှာ ပြထားသလို ရေးတဲ့အခါ ဘာ error မှ ပြနေမှာ မဟုတ်မယ့် run လိုက်တဲ့အခါ အခုလိုမျိုး error ကို ပြနေမှာပဲ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။
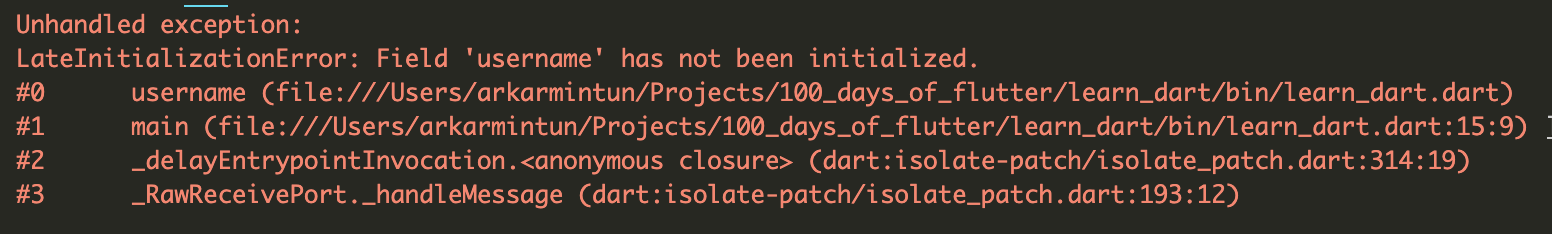
late ကို သုံးလိုက်တာက dart compiler ကို ဒီ value က အခုလောလောဆယ် မသတ်မှတ်ထားရသေးပေမယ့် access လုပ်တဲ့အချိန်မှာ သတ်မှတ်ပြီးသား ဖြစ်ကို ဖြစ်နေမှာလို့ ပြောလိုက်တာနဲ့ တူပါတယ်။
အခုလိုမျိုး ပြင်ရေးလိုက်ရင်တော့ error တက်တော့မှာ မဟုတ်ပါဘူး။
late String username;
void main() {
username = "Aung Aung";
print(username.length);
}
// Output:
// 9ဒီတော့ ဘာလို့ late keyword ကို သုံးနေကြသေးတုန်းဆိုတဲ့ မေးခွန်း မေးစရာ ရှိလာပါပြီ။ သူ့ကိုတော့ dependency injection လိုမျိုးတွေ လုပ်တဲ့အချိန်၊ flutter မှာဆို controller တွေ အတွက် သုံးကြပါတယ်။
class _MyFormState extends State<MyForm> {
late AnimationController _animController;
late TextEditingController _nameController;
late TextEditingController _emailController;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_animController = AnimationController(vsync: this, duration: Duration(seconds: 1));
_nameController = TextEditingController(text: widget.name);
_emailController = TextEditingController(text: widget.email);
}
@override
void dispose() {
_animController.dispose();
_nameController.dispose();
_emailController.dispose();
super.dispose();
}
}@riverpod
class UserNotifier extends _$UserNotifier {
late final AuthRepository _authRepo;
@override
Future<User?> build() async {
_authRepo = ref.read(authRepositoryProvider);
return _authRepo.getCurrentUser();
}
}Flutter app တွေ ရေးတဲ့အခါမှာ late နဲ့ ပတ်သက်တာတွေ အသေးစိတ် ရှင်းပြပေးသွားပါမယ်။ အခုတော့ late usage ရှိပြီးတော့ သူ့ကို variable define လုပ်တဲ့အခါ သုံးတာဖြစ်ကြောင်း သိရင် ရပါပြီ။
Null Safety Operators
Nullable အကြောင်း ပြောပြီးပြီဆိုတော့ null ဖြစ်နေတဲ့ value တွေကို ဘယ်လို ကိုင်တယ်ကြမလဲဆိုတာ ဆက်ပြီး ကြည့်လိုက်ကြအောင်ပါ။
Null-Aware Operator (??)
ဒါကိုတော့ value ကို access လုပ်ပြီးတော့ တကယ်လို့ null ဖြစ်နေခဲ့ရင် fallback အနေနဲ့ သတ်မှတ်ဖို့ သုံးပါတယ်။
String? userName;
String display = userName ?? 'Guest'; // If null, use 'Guest'Null-Aware Assignment (??=)
ဒါကိုတော့ value ကို access လုပ်ခါနီးမှာ value အနေနဲ့ မရှိရင် fallback အနေနဲ့ သတ်မှတ်ဖို့ သုံးလို့ရပါတယ်။ အပေါ်နဲ့ ကွာတာက variable နောက်တခုထဲကို သွားပြီးတော့ မထည့်ဘဲနဲ့ လက်ရှိ ရှိပြီးသား variable ကိုပဲ စစ်ပြီးတော့ value မသတ်မှတ်ထားတဲ့အခါ assign လုပ်သွားတာမျိုး ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ တကယ်လို့ value သတ်မှတ်ပြီးသား ရှိတယ်ဆိုရင်တော့ ထပ်ပြီးတော့ update မလုပ်တော့ပါဘူး။
int? score;
score ??= 0; // Only assigns if score is null
score ??= 1; // nothing happen since the value has been assignedNull-Aware Access (?.)
ဒါကတော့ null ဖြစ်နိုင်တဲ့ value ကို ဖတ်ပြီးတော့ တကယ်လို့ null ဖြစ်နေတယ်ဆို null ကို သတ်မှတ်လို့ရတဲ့နေရာတွေမှာ သုံးပါတယ်။ null မဟုတ်ဘူးဆိုရင်တော့ သတ်မှတ်ထားတဲ့ function ပဲဖြစ်ဖြစ်၊ getter ပဲ ဖြစ်ဖြစ်ကို ဆက်ပြီးတော့ လုပ်ဆောင်ပေးသွားမှာ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။
String? email;
int? length = email?.length; // Returns null if email is nullNull Assertion (!)
ဒါကတော့ null အနေနဲ့ သတ်မှတ်ထားပေမယ့် value ရှိနေမှာ သေချာတယ်ဆိုတဲ့ နေရာတွေမှာ သုံးပါတယ်။ value ရှိကိုရှိတယ်လို့ ပြောလိုက်တာနဲ့ တူပါတယ်။ late နဲ ဆင်သယောင်ရှိပေမယ့် ဒီမှာတော့ အစက variable သတ်မှတ်တုန်းက nullable အနေနဲ့ သတ်မှတ်ထားတာပါ။ access လုပ်တော့မယ့်အချိန်မှ သတ်မှတ်ထားတာ သေချာကြောင်း ပြောလိုက်တာနဲ့ တူပါတယ်။
String? definitelyHasValue = 'Hello';
String unwrapped = definitelyHasValue!; // I'm 100% sure it's not nullအပေါ်မှာ ဆွေးနွေးသွားတာတွေ အားလုံးကို တချက်လောက် ဥပမာလေးတွေနဲ့ ကြည့်ကြည့်ရအောင်ပါ။
void main() {
// ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
// 1️⃣ BASIC NULLABLE VS NON-NULLABLE
// ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
print('1️⃣ BASIC NULLABLE VS NON-NULLABLE');
print('─────────────────────────────────────');
String definitelyHasValue = 'Hello Flutter';
String? mightBeNull;
String? hasValueNow = 'I exist';
print('Non-nullable: $definitelyHasValue');
print('Nullable (null): $mightBeNull');
print('Nullable (has value): $hasValueNow\n');
// ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
// 2️⃣ NULL-AWARE OPERATORS (?., ??, ??=, !)
// ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
print('2️⃣ NULL-AWARE OPERATORS');
print('─────────────────────────────────────');
String? username;
String? email = 'user@example.com';
// ?. (Null-aware access)
int? usernameLength = username?.length;
int? emailLength = email?.length;
print('Username length: $usernameLength (null because username is null)');
print('Email length: $emailLength\n');
// ?? (If-null operator)
String displayName = username ?? 'Guest User';
print('Display name: $displayName\n');
// ??= (Null-aware assignment)
String? theme;
theme ??= 'dark'; // Assigns because theme is null
print('Theme after first ??=: $theme');
theme ??= 'light'; // Does nothing because theme already has value
print('Theme after second ??=: $theme (still dark!)\n');
// ! (Bang operator - use carefully!)
String definiteEmail = email!; // We're 100% sure email isn't null
print('Unwrapped email: $definiteEmail\n');
// ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
// 3️⃣ LATE VARIABLES
// ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
print('3️⃣ LATE VARIABLES');
print('─────────────────────────────────────');
late String apiKey;
late final String configUrl;
// Initialize them later
apiKey = 'secret-key-12345';
configUrl = 'https://api.example.com';
print('API Key: $apiKey');
print('Config URL: $configUrl');
// Can reassign late (but not late final)
apiKey = 'new-secret-key';
print('Updated API Key: $apiKey\n');
// configUrl = 'new-url'; // ❌ Would error: can't reassign late final
// ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
// 4️⃣ TYPE PROMOTION & FLOW ANALYSIS
// ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
print('4️⃣ TYPE PROMOTION & FLOW ANALYSIS');
print('─────────────────────────────────────');
String? possiblyNullName = getNameFromDatabase();
// Before null check: possiblyNullName is String?
// print(possiblyNullName.length); // ❌ Would error
if (possiblyNullName != null) {
// After null check: Dart promotes possiblyNullName to String!
print('Name: $possiblyNullName');
print('Length: ${possiblyNullName.length}'); // ✅ No ! needed
print('Uppercase: ${possiblyNullName.toUpperCase()}\n');
} else {
print('No name found\n');
}
// ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
// 5️⃣ NULLABLE COLLECTIONS
// ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
print('5️⃣ NULLABLE COLLECTIONS');
print('─────────────────────────────────────');
// List of nullable strings
List<String?> names = ['Alice', null, 'Bob', null, 'Charlie'];
print('Original list: $names');
// Nullable list of strings
List<String>? optionalTags;
print('Optional tags (null): $optionalTags');
// Nullable list of nullable strings
List<String?>? maybeNames;
print('Maybe names (null): $maybeNames\n');
// Filter out nulls
List<String> nonNullNames = names.whereType<String>().toList();
print('Non-null names: $nonNullNames');
// Or using where
List<String> filtered = names
.where((name) => name != null)
.map((name) => name!) // Safe because we checked
.toList();
print('Filtered names: $filtered\n');
// Null-aware spread operator
List<String>? additionalItems = ['Extra1', 'Extra2'];
List<String>? nullItems;
List<String> combined = [
'Required',
...?additionalItems, // Spreads if not null
...?nullItems, // Does nothing because null
];
print('Combined list: $combined\n');
// ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
// 6️⃣ NULLABLE MAPS
// ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
print('6️⃣ NULLABLE MAPS');
print('─────────────────────────────────────');
Map<String, String?> userProfile = {
'name': 'Alice',
'email': 'alice@example.com',
'bio': null,
'website': null,
};
print('Name: ${userProfile['name']}');
print('Bio: ${userProfile['bio'] ?? 'No bio provided'}');
// Safe map access
String? bio = userProfile['bio'];
int? bioLength = bio?.length;
print('Bio length: $bioLength\n');
// ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
// 7️⃣ FUNCTIONS WITH NULLABLE PARAMETERS & RETURNS
// ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
print('7️⃣ FUNCTIONS WITH NULLABLE PARAMETERS');
print('─────────────────────────────────────');
greetUser('Alice');
greetUser(null);
print('');
String? result1 = findUserById('123');
String? result2 = findUserById('999');
print('User 123: $result1');
print('User 999: ${result2 ?? 'Not found'}\n');
// ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
// 8️⃣ ASYNC NULL SAFETY
// ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
print('8️⃣ ASYNC NULL SAFETY');
print('─────────────────────────────────────');
asyncNullSafetyDemo();
// ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
// 9️⃣ PATTERN MATCHING WITH NULL CHECKS
// ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
print('\n9️⃣ PATTERN MATCHING WITH NULL CHECKS');
print('─────────────────────────────────────');
String? status = getStatus();
// Modern switch expression with null handling
String message = switch (status) {
String value when value == 'active' => 'User is active',
String value when value == 'inactive' => 'User is inactive',
String value => 'Unknown status: $value',
null => 'No status available',
};
print('Status message: $message\n');
// ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
// 🔟 DEFINITE ASSIGNMENT
// ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
print('🔟 DEFINITE ASSIGNMENT');
print('─────────────────────────────────────');
int score;
bool isWeekend = DateTime.now().weekday > 5;
if (isWeekend) {
score = 100;
} else {
score = 50;
}
// Dart knows score is definitely assigned here
print('Score: $score\n');
// ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
// 1️⃣1️⃣ CHAINING NULL-AWARE OPERATORS
// ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
print('1️⃣1️⃣ CHAINING NULL-AWARE OPERATORS');
print('─────────────────────────────────────');
String? userInput;
String? systemDefault = 'default-theme';
String hardcodedFallback = 'light';
String finalTheme = userInput ?? systemDefault ?? hardcodedFallback;
print('Final theme: $finalTheme\n');
// ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
// 1️⃣2️⃣ PRACTICAL EXAMPLE: PROCESSING USER DATA
// ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
print('1️⃣2️⃣ PRACTICAL EXAMPLE: USER DATA PROCESSING');
print('─────────────────────────────────────');
processUserData(
name: 'Alice',
age: null,
email: 'alice@example.com',
hobbies: null,
);
print('');
processUserData(
name: 'Bob',
age: 30,
email: null,
hobbies: ['reading', 'gaming'],
);
print('\n═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════');
print('✅ NULL SAFETY DEMO COMPLETE!');
print('═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════');
}
// ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
// HELPER FUNCTIONS
// ═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════
String? getNameFromDatabase() {
// Simulating database lookup
return DateTime.now().second % 2 == 0 ? 'John Doe' : null;
}
void greetUser(String? name) {
// Function accepting nullable parameter
String greeting = 'Hello, ${name ?? 'Guest'}!';
print(greeting);
}
String? findUserById(String id) {
// Function returning nullable value
Map<String, String> users = {'123': 'Alice', '456': 'Bob'};
return users[id]; // Returns null if not found
}
Future<void> asyncNullSafetyDemo() async {
print('Fetching user data...');
String? username = await fetchUsername();
if (username != null) {
print('Welcome back, $username');
} else {
print('Welcome, Guest');
}
// Chaining with null-aware
String display = username ?? 'Anonymous';
print('Display name: $display');
}
Future<String?> fetchUsername() async {
// Simulating API call
await Future.delayed(Duration(milliseconds: 100));
return DateTime.now().second % 2 == 0 ? 'AsyncUser' : null;
}
String? getStatus() {
List<String?> statuses = ['active', 'inactive', null];
return statuses[DateTime.now().second % 3];
}
void processUserData({
required String name,
int? age,
String? email,
List<String>? hobbies,
}) {
print('Processing data for: $name');
// Type promotion in action
if (age != null) {
print(' Age: $age');
// age is promoted to int (non-nullable) here
int yearsTo100 = 100 - age;
print(' Years to 100: $yearsTo100');
} else {
print(' Age: Not provided');
}
// Null-aware access
print(' Email: ${email ?? 'No email'}');
// Null-aware spread in list
List<String> info = [
'Name: $name',
if (age != null) 'Age: $age',
...?hobbies?.map((h) => 'Hobby: $h'),
];
print(' Summary: ${info.join(', ')}');
}
ဒီနေ့ Day 5 အတွက်ကတော့ ဒီလောက်ပဲ ဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ အဆုံးထိ ဖတ်ပေးတဲ့အတွက် အများကြီး ကျေးဇူးတင်ပါတယ်။ နားမလည်တာတွေ အဆင်မပြေတာတွေ ရှိခဲ့ရင်လဲ အောက်မှာပေးထားတဲ့ discord server ထဲမှာ လာရောက်ဆွေးနွေးနိုင်ပါတယ်။ နောက်နေ့တွေမှာလဲ ဆက်လက်ပြီး sharing လုပ်သွားပေးသွားမှာ ဖြစ်တဲ့အတွက် subscribe လုပ်ထားဖို့ ဖိတ်ခေါ်ပါတယ်။
- Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/@arkarmintun
- Newsletter: https://arkar.dev/
- Discord: https://discord.gg/3xUJ6k6dkH
